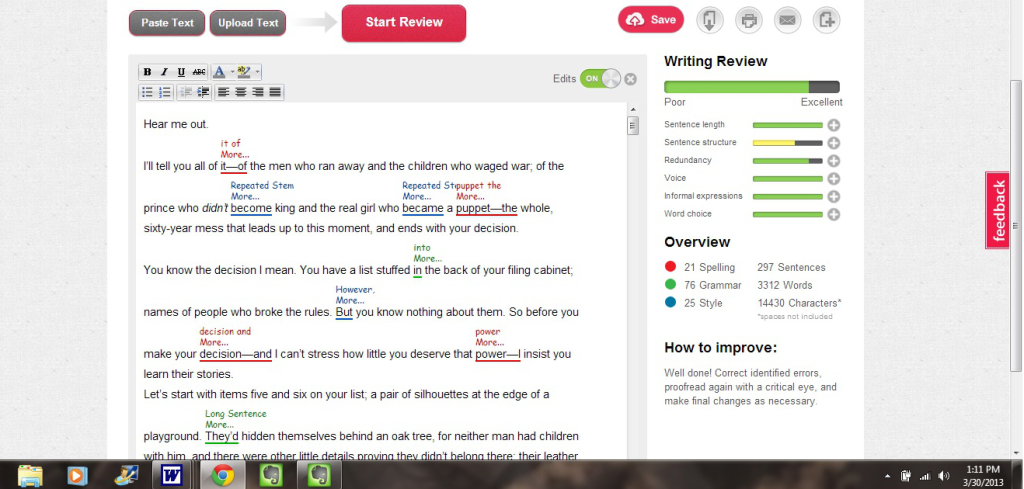
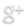You go to visit some friends you haven’t seen in awhile, and find yourself sandwiched between your hosts on the couch with a giant scrapbook over your lap like a seat belt, as they show off the half million pictures of snow-capped mountains they snapped on their most recent vacation.
While we introverts may actually appreciate this in lieu of starting a conversation, it isn’t exactly entertainment. And here’s the awful truth:
You may be doing it to your readers.
In writing, this sin is known as scenic description. No matter how artfully you describe those snow-capped mountains, if it’s longer than a few sentences and not relevant to the plot, it’s boring.
The difference is, your readers don’t have to politely “ooh” and “ah” for two hundred pages. They can simply shut the book.
That brings us to two rules for scenic description:
Rule Number One: Less is more.
Don’t interrupt the climax with a description of janitorial supplies purchased in bulk; just give the reader a sense of the area—if possible, mix it with action—and move on.
Rule Number Two: Scenic description should do more than describe scenery.
Whenever possible, make description do double duty: for instance, use it to illustrate your character’s mood.
This doesn’t mean make it sunny when your hero is happy and rainy when he’s sad: you can use any scene and any type of weather to convey any mood, simply by changing your tone. A sunny day can either warm the cockles of his heart or blithely mock his pain.
Let’s take a noisy tavern as an example:
The creak and slam of the door cut out the howling wind and heralded the music within, so loud he had to shout his order in the barmaid’s ear before taking a seat by the great fire. The crackling of the wood lay down a kind of beat for the lutenist at the other end of the room, who dared the revelers to keep up with his quick fingers. Thudding boots made empty tankards dance on the tables, and spirited singing from the depths of barrel chests dissolved into thunderclap laughter each time a lyric was slurred.
Versus this:
The hinges screeched, the door slammed, and the clamorous indoors suddenly choked off the soft moan of the evening breeze. He had to scream his order to the barmaid, and even as he huddled, sweating, next to the coughing fire, he couldn’t hear his own thoughts over the revelers at the other end of the room, whose discordant bellows and guffaws shook the rafters, dwarfing the lute accompaniment to a tinny whisper.
Notice the facts are the same, but the words I use to deliver those facts have different connotations. First, the positive connotations of words like heralded, great, quick, dance, spirited, laughter. Then the connotations feel of words like clamorous, choking, scream, sweating, coughing, discordant, guffaws, tinny.
The result: you feel, rather than read, the mood. Another example of Show, Don’t Tell.
What are some other ways scenic description can do double-duty? Tell me in the comments!
—